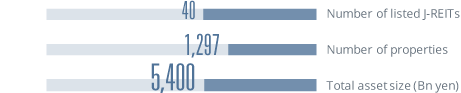-
NOV The amendment of the Investment Trust Act enables the creation of J-REITs.

-
SEP The first two J-REITs, Nippon Building Fund Inc. and Japan Real Estate Investment Corporation, are listed on the TSE.



JAN Inauguration of U.S. President George W. Bush
SEP 9/11 Attacks.
-
MAR The first retail REIT, Japan Retail Fund Investment Corporation, is listed.

-
JUN The first diversified REIT, ORIX JREIT, Inc. is listed.

-
JUN The QUICK REIT Index is launched.
-
DEC The Association for Real Estate Securitization (ARES) is established.



JAN Euro banknotes and coins are introduced.
MAR Bank of Japan Governor Toshihiko Fukui assumes office.

-
APR The TSE REIT Index is launched.
-
MAY J-REITs are included in the MSCI Japan Index for the first time.
-
JUL Rule change of The Investment Trusts Association Japan allows creation of J-REIT funds, mutual funds which invest in J-REITs.
-
DEC Osaka Securities Exchange opens J-REIT market.


MAR Outbreak of Iraq War
-
FEB J-REIT market capitalization reaches 1 trillion yen.

-
MAR The first residential REIT, Nippon Residential Investment Corporation, is listed.

-
AUG Fukuoka Stock Exchange opens J-REIT market.
-
DEC JASDAQ opens J-REIT market.
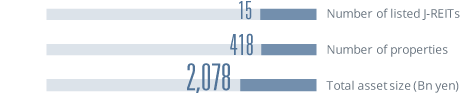

OCT Niigata Chuetsu Earthquake.
-
MAY The first logistics REIT, Japan Logistics Fund, Inc., is listed.

-
JUN The first region-specific REIT, Fukuoka REIT Corporation, is listed.

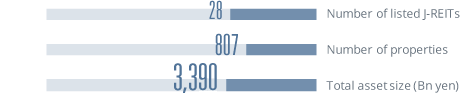

MAR Expo 2005 Aichi, Japan.
OCT Japan Post privatization law passed.
-
FEB The first hotel REIT, Japan Hotel and Resort Investment Corporation, is listed.

FEB U.S. Federal Reserve Board (FRB) Chairman Ben Bernanke assumes office.
-

SEP ARES holds the commemorative seminar.
-
JAN J-REIT market capitalization reaches 5 trillion yen.

-
MAY TSE REIT Index hits a record high of 2612.98 on May 31.
-
SEP Enforcement of Financial Instruments and Exchange Law.
-
OCT The first industrial REIT, Industrial & Infrastructure Fund Investment Corporation, is listed.



-
MAY TSE changes listing requirements on J-REITs, allowing them to invest in overseas properties.
-
SEP First ETF linked to the TSE REIT Index listed.
-
SEP The collapse of Lehman Brothers triggers the global financial crisis (GFC). The impact spreads to the J-REIT market.
-
OCT First J-REIT files for civil rehabilitation proceedings and is delisted.
-
OCT TSE REIT Index (excluding dividend payment) falls to a record low of 704.46 on October 28.


APR Bank of Japan Governor Masaaki Shirakawa assumes office.
-
JAN Institutional arrangements for J-REIT mergers progresses, such as legal amendments related to negative goodwill and merger grants.
-
SEP The turmoil in global financial markets and the credit crunch have also put a squeeze on J-REIT funding, and fearing that a dysfunctional J-REIT market would have a negative impact on the real estate market as a whole and the Japanese economy, the government established the Real Estate Market Stabilization Fund, a public-private partnership as part of its economic crisis countermeasures. The announcement effect for market stabilization was significant.


JAN Inauguration of U.S. President Barack Obama.
SEP The Hatoyama Cabinet is formed with the change of government to the Democratic Party of Japan.

-
FEB First J-REIT merger completed.
-
OCT BOJ establishes Asset Purchase Fund to purchase a variety of assets including ETFs and J-REITs.


・European debt crisis spreads, starting with Greece.
MAR Great East Japan Earthquake.
-


SEP ARES holds the commemorative symposium.

-
APR The first J-REIT IPO since GFC is made by Kenedix Residential Investment Corporation.

-
DEC Daiwa House Residential Investment Corp. announces the split of investment units. It is the first case for J-REITs not associated with a merger.


DEC The second Abe Cabinet is formed with a change of government to a coalition of the Liberal Democratic Party and New Komeito.

-
A series of REITs investing in logistics facilities have been listed, and logistics assets now account for about 10% of the total assets of J-REITs. Reflecting diversification, the share of office properties has dropped to less than 50%.



MAR Bank of Japan Governor Haruhiko Kuroda assumes office.
DEC Number of foreign visitors to Japan exceeds 10 million annually for the first time.

-
APR Government Pension Investment Fund (GPIF) starts investing in J-REITs.
-
JUN AEON REIT Investment Corporation becomes the first J-REIT which acquires an overseas property.

-
JUN Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT) announces the Guideline for Utilizing Healthcare REIT for Senior Housings, etc.
-
NOV The first healthcare REIT, Nippon Healthcare Investment Corporation, is listed.


JAN NISA, a Japanese tax-free investment program for individuals, launched.
FEB U.S. Federal Reserve Board (FRB) Chairman Janet Yellen assumes office.
APR Consumption tax rate raised from 5% to 8%.
-
MAR J-REIT market grows to the world's second-largest REIT market by market capitalization.
-
APR Allowance for Temporary difference Adjustment (ATA) is introduced in order to avoid double taxation caused by the tax-accounting mismatch in investment corporations.
-
JUN MLIT announces the Guideline for Utilizing Healthcare REIT for Hospitals' Real Estate Assets.
-
OCT The first case of merger between 3 J-REITs is completed: Nomura Real Estate Master Fund Inc., Nomura Real Estate Office Fund, Inc., and Nomura Real Estate Residential Fund, Inc.




-
JAN BOJ introduces "Quantitative and Qualitative Monetary Easing with a Negative Interest Rate." It gives a momentum to the J-REIT market.
-
MAY BOJ submits its first large shareholding report on J-REITs.
-
Diversification of J-REITs' investment targets further progressed with the listing of REITs focusing on logistics, hotels, hot springs, regional properties, etc.

APR Kumamoto Earthquake.
JUN U.K. votes to leave the EU in referendum.
OCT Foreign visitors to Japan exceeded 20 million per year for the first time.
-


OCT ARES holds the commemorative symposium.
OCT Foreign visitors to Japan exceeded 20 million per year for the first time.

-
JUN Share buybacks, made possible by a 2013 legal amendment, was implemented for the first time.
-
MAY The Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi UFJ securitized loan claims to J-REITs.
-
NOV Healthcare & Medical Investment Corporation acquires a hospital real estate for the first time among J-REITs.



JAN Inauguration of U.S. President Donald Trump.
JUL GPIF launches ESG Investments.

-
MAR TSE REIT Core Index is launched.
-
MAY Japan Retail Fund Investment Corporation issues its first green bonds as a J-REIT.
-
MAY The net asset value of J-REIT ETFs (ETFs linked to domestic REIT indices) exceeds 1 trillion yen.


FEB Federal Reserve Board (FRB) Chairman Jerome Powell assumes office.
FEB U.S. Federal Reserve Board (FRB) Chairman Jerome Powell assumes office.

-
JUL J-REIT market capitalization reaches 15 trillion yen.
-
JUL TSE REIT Index recovered to the 2,000-point level (first time in 11 years and 7 months since December 2007 on a closing basis).

MAY Japanese era name changes to REIWA from Heisei.
MAY Japanese era name changes to REIWA from Heisei.
OCT Consumption tax rate increased to 10%.
-
MAR The TSE REIT index falls sharply due to the turmoil in the financial capital market triggered by the spread of COVID-19 infections.
-
JUL Nikkei Inc. starts calculating "Nikkei ESG-REIT Index" and "Nikkei High Yield REIT Index".Also, the Tokyo Stock Exchange launches "TSE REIT Logistics Focus Index".
-
SEP FTSE Russell begins to include J-REITs in the FTSE Global Equity Index Series (GEIS).

MAR The World Health Organization (WHO) declares the COVID-19 outbreak a pandemic.
APR The first COVID-19 state of emergency is declared by the Japanese government.
-
APR First hostile takeover bid for a J-REIT is launched.
-
APR Japan Metropolitan Fund Investment Corporation acquires investment units of a Japanese private REIT for the first time among listed J-REITs.
JAN Inauguration of U.S. President Joe Biden.
FEB Nikkei 225 tops 30,000 for the first time since 1990.
JUL Tokyo 2020 Olympics is held after a one-year postponement.
AUG Tokyo 2020 Paralympics is held after a one-year postponement.
-


SEP ARES holds the commemorative symposium.
-
NOV Invesco Office J-REIT, Inc. is delisted after a successful takeover bid from its sponsor group, and it marks the first going-private transaction of a J-REIT.

-
MAR U.S. investment firm KKR acquires Mitsubishi Corp.-UBS Realty, an asset manager of two J-REITs for 230 billion yen ($2 billion).
-
APR Tokyo Stock Exchange starts trading in three new stock market segments: Prime, Standard and Growth Markets
FEB Russia invades Ukraine.
JUN Cabinet decides to set a goal of increasing the total assets of J-REITs, etc. to approximately 40 trillion yen by around 2030.
OCT Removal of COVID-19 entry restrictions for foreign nationals.
-
JUL Bank of Japan (BOJ) revises its Yield Curve Control (YCC) policy.
APR Bank of Japan Governor Ueda Kazuo assumes office.
MAY COVID-19 legal status moves to "Class 5", the same category as seasonal influenza.
OCT Clashes erupt between Israel and the Palestinian militants.
-
MAR The Bank of Japan decides to lift its negative interest rate policy, eliminate yield curve control, and terminate new purchases of ETFs and J-REITs.
-
MAY First U.S. real estate investment by a J-REIT
-
NOV Tokyo Stock Exchange extends trading hours by 30 minutes and introduces closing auction
-
J-REITs' buybacks hit record high
JAN New NISA, a Japanese tax-free investment program for individuals, launched
Noto Peninsula Earthquake
FEB Nikkei 225 reaches all-time high for the first time in 34 years
MAY Long-term interest rates reach 1% for the first time in 11 years
JUL Issuance of new banknotes begins; portrait on 10,000-yen bill changed to that of Shibusawa Eiichi
SEP U.S. Fed decides to cut interest rates for the first time in 4.5 years
OCT First minority government in 30 years inaugurated
-
JAN Bank of Japan raised its policy rate to 0.5%
-
JAN 3D Investment launched an unsolicited tender offer (TOB) for NTT Urban Development REIT Investment Corporation
-
FEB 3D Investment launched an unsolicited tender offer (TOB) for Hankyu Hanshin REIT, Inc.
-
JUN Financial Services Agency revised its “Q&A on Investment Corporations,” clarifying the eligibility of certain data center-related facilities as real estate assets
-
AUG Kasumigaseki Hotel REIT Investment Corporation was listed, marking the first J-REIT IPO in approximately four years
-
SEP Bank of Japan decided to sell its holdings of ETFs and J-REITs in the market
-
NOV The Tokyo Stock Exchange REIT Index recovered to the 2,000-point level for the first time in three years
-
DEC The Bank of Japan raised its policy rate to 0.75%. The yield on 10-year Japanese government bonds rose into the 2% range.
JAN U.S. President Donald Trump inaugurated for a second term
APR The United States announced the introduction of reciprocal tariffs
APR Expo 2025 Osaka, Kansai opened
JUL In the House of Councillors election, the ruling Liberal Democratic Party and Komeito suffered major losses, resulting in a minority government in both houses of the Diet
OCT Komeito dissolved its coalition with the Liberal Democratic Party. The LDP subsequently formed a coalition government with Japan Innovation Party, and a cabinet led by Sanae Takaichi was inaugurated (Japan’s first female prime minister)
OCT The Nikkei 225 surpassed the 50,000 mark for the first time
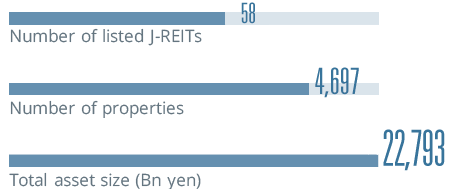
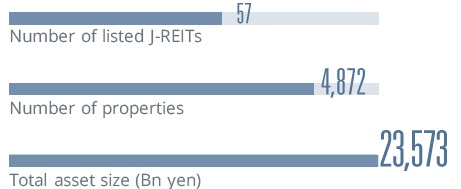
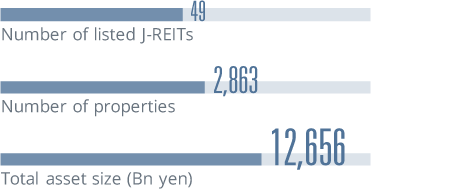
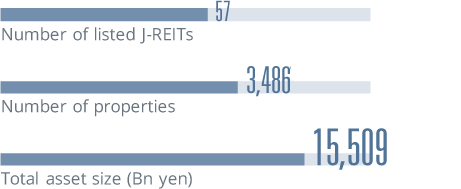
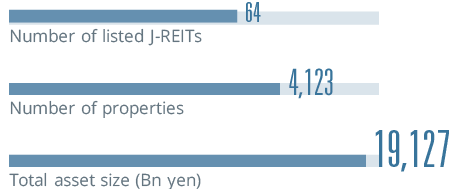
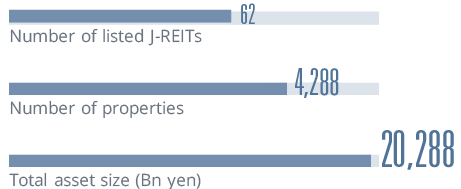
*The data is as of the end of each year

The amendment of the Investment Trust Act enables the creation of J-REITs.
Since REITs (Real Estate Investment Trust) originated in the United States in 1960, various countries have introduced them. In Japan, it became possible to form REITs in 2000 with the amendment to the Act on Investment Trusts and Investment Corporations which enabled investment trusts to invest in real estate.

Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE) creates the J-REIT market.
With the amendment to the Act on Investment Trusts and Investment Corporations, the TSE developed the rules for creating the J-REIT market. With the TSE’s preparation, the environment was ready for J-REITs to be listed on the TSE.

First J-REIT files for civil rehabilitation proceedings and is delisted.
October 9, 2008, New City Residence Investment Corporation filed for civil rehabilitation proceedings. The main reason was not a problem in the real estate leasing business, but rather a cash management problem, such as procurement of funds for settlement of assets to be acquired and repayment of loans. Learning from these cases, guidelines were established that call for careful handling of recent purchase agreements, known as forward commitments, while also taking into consideration the financial impact and other factors, thereby improving the soundness of the J-REIT market.

ARES holds the 1st J-REITs Fair for Individual Investors.
Since the awareness of J-REITs among individual investors is lower than that of other financial products, we hosted this event with the aim of promoting the attractiveness of J-REITs, which allow investors to start real estate investment with a small amount of money and offer stable dividends. Since then, the event has been held annually until 2019, and has been well received as an opportunity for individual investors to obtain information on J-REITs in one place.

First J-REIT merger completed.
On February 1, 2010, Tokyo Growth REIT Investment Corporation and LCP Investment Corporation merged and changed its name to Invincible Investment Corporation. Starting with this merger, a total of seven mergers took place in 2010.

BOJ establishes Asset Purchase Fund to purchase a variety of assets including ETFs and J-REITs.
In order to further promote monetary easing, the BOJ decided to establish a fund to purchase a variety of financial assets, etc., with the aim of encouraging a decline in market interest rates and a reduction in various risk premiums, and J-REITs were also included in the scope of purchases.

J-REIT market capitalization reaches 10 trillion yen.
On November 28, 2014, the market capitalization of J-REITs exceeded 10 trillion yen for the first time. ARES had one goal of a market size of 10 trillion yen, as expanding the size of the market is considered important for expanding the investor base and stabilizing the market.

J-REIT market grows to the world's second-largest REIT market by market capitalization.
ARES conducts an annual survey on the size of the global REIT market as of the end of March. In this survey, J-REITs ranked second in the world for the first time in terms of market capitalization (the U.S. ranked first).
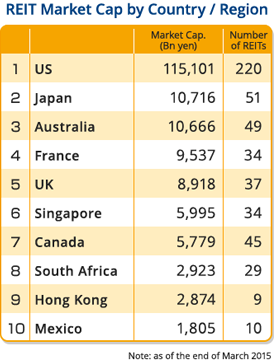

The Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi UFJ securitized loan claims to J-REITs.
For the first time, BTMU has securitized the credit risk of loan receivables for J-REITs and sold them to institutional investors. This is a new move that will provide a new product to investors who are experiencing investment difficulties due to ultra-low interest rates, and will also lead to a reduction of loan risk for the bank. Subsequently, Sumitomo Mitsui Trust Bank, Limited has also undertaken a similar securitization initiative.

Japan Retail Fund Investment Corporation issues its first green bonds as a J-REIT.
In recent years, environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues have been attracting increasing attention in the global capital markets, and ESG-related initiatives are expanding in the J-REIT market as well. Green bonds and green loans are financing methods in which funds are used for environmentally friendly projects, and were used for the first time in J-REITs in 2018.

The TSE REIT index falls sharply due to the turmoil in the financial capital market triggered by the spread of COVID-19 infections.
The TSE REIT index hits the year's high of 2,250.65 points on February 20, but falls to 1,145.53 points on March 19.

FTSE Russell begins to include J-REITs in the FTSE Global Equity Index Series (GEIS).
The Inclusion of J-REITs into the FTSE Global Equity Index Series begins in September 2020 and will be implemented in four tranches by June 2021. The inclusion is expected to expand the range of investors of J-REITs.

First hostile takeover bid for a J-REIT is launched.
Starwood Capital Group launched a takeover bid (TOB) to take Invesco Office J-REIT Investment Corporation private. This was the first hostile TOB conducted without the approval of a J-REIT, but the TOB failed because the number of investment units tendered did not meet the minimum number of units to be purchased.

Bank of Japan (BOJ) revises its Yield Curve Control (YCC) policy.
The Bank of Japan decided to revise its yield curve control (YCC) policy at its July 28 Monetary Policy Meeting, raising the de facto ceiling on long-term interest rates from 0.5% to 1.0%. Furthermore, in October 2023, the BOJ revised the YCC again, allowing long-term interest rates to remain above 1% to a certain degree.

First U.S. real estate investment by a J-REIT
Sekisui House REIT, Inc. acquired a multi-family residential building in Seattle, U.S. This was the first investment in U.S. real estate by a J-REIT, and the first overseas real estate investment itself in about six years.

J-REITs' buybacks hit record high
In 2024, a total of 22 J-REITs resolved to repurchase their own investment units, and a record 100 billion yen or more was allocated for such repurchases.

3D Investment launched an unsolicited tender offer (TOB) for Hankyu Hanshin REIT, Inc.
Amid persistently low investment unit prices, Singapore-based investment fund 3D Investment Partners launched successive unsolicited tender offers for two J-REITs. Neither offer was aimed at taking the REITs private, and in both cases the respective investment corporations maintained a neutral stance. Although both tender offers ultimately failed, the moves renewed market attention to valuation levels in the J-REIT sector.

Financial Services Agency revised its “Q&A on Investment Corporations,” clarifying the eligibility of certain data center-related facilities as real estate assets
In June 2025, the Japanese government approved a cabinet decision stating that, in order to promote domestic investment in data centers and provide diversified investment vehicles including real estate, it would develop the necessary framework to allow REITs to incorporate data centers into their portfolios.
In response, on June 27, 2025, the Financial Services Agency revised its “Q&A on Investment Corporations,” clarifying that certain types of data center-related facilities meeting specified installation criteria qualify as “real estate,” the primary investment target of real estate investment corporations.
Unlike traditional asset types such as office buildings, data centers derive a relatively larger portion of their value from equipment—such as power supply, cooling, and network infrastructure—rather than from land and building structures themselves. The clarification addressed one of the key regulatory issues for establishing data center-focused REITs in Japan.

Bank of Japan decided to sell its holdings of ETFs and J-REITs in the market
On September 19, 2025, the Bank of Japan announced its decision to gradually sell ETFs and J-REITs that it had previously purchased, in small amounts over an extended period. For the time being, the proportion of sales relative to total market trading value is set at approximately 0.05%.
Regarding J-REITs, sales are to be conducted at a pace of about JPY 5 billion per year (book value), based on prices formed on exchange markets. Actual sales of ETFs and J-REITs commenced in January 2026.
The J-REIT market has achieved a significant growth since its inception going through difficulties such as the Global Financial Crisis and the Great East Japan Earthquake in 2011. J-REITs have provided investors with new investment opportunities as financial products and have played a social role by contributing to the urban regeneration, local revitalization and the individual’s asset formation. The J-REIT market is expected to develop further to make a greater contribution to the society overcoming COVID-19 crisis.